How to Choose the Right HPLC Vial Septa for Your Solvent
Factors to Consider When Selecting HPLC Vial Septa
1. Chemical compatibility
The first thing to consider is the chemical compatibility of the septum material with the solvents you plan to use. Different materials have different tolerances to chemicals:
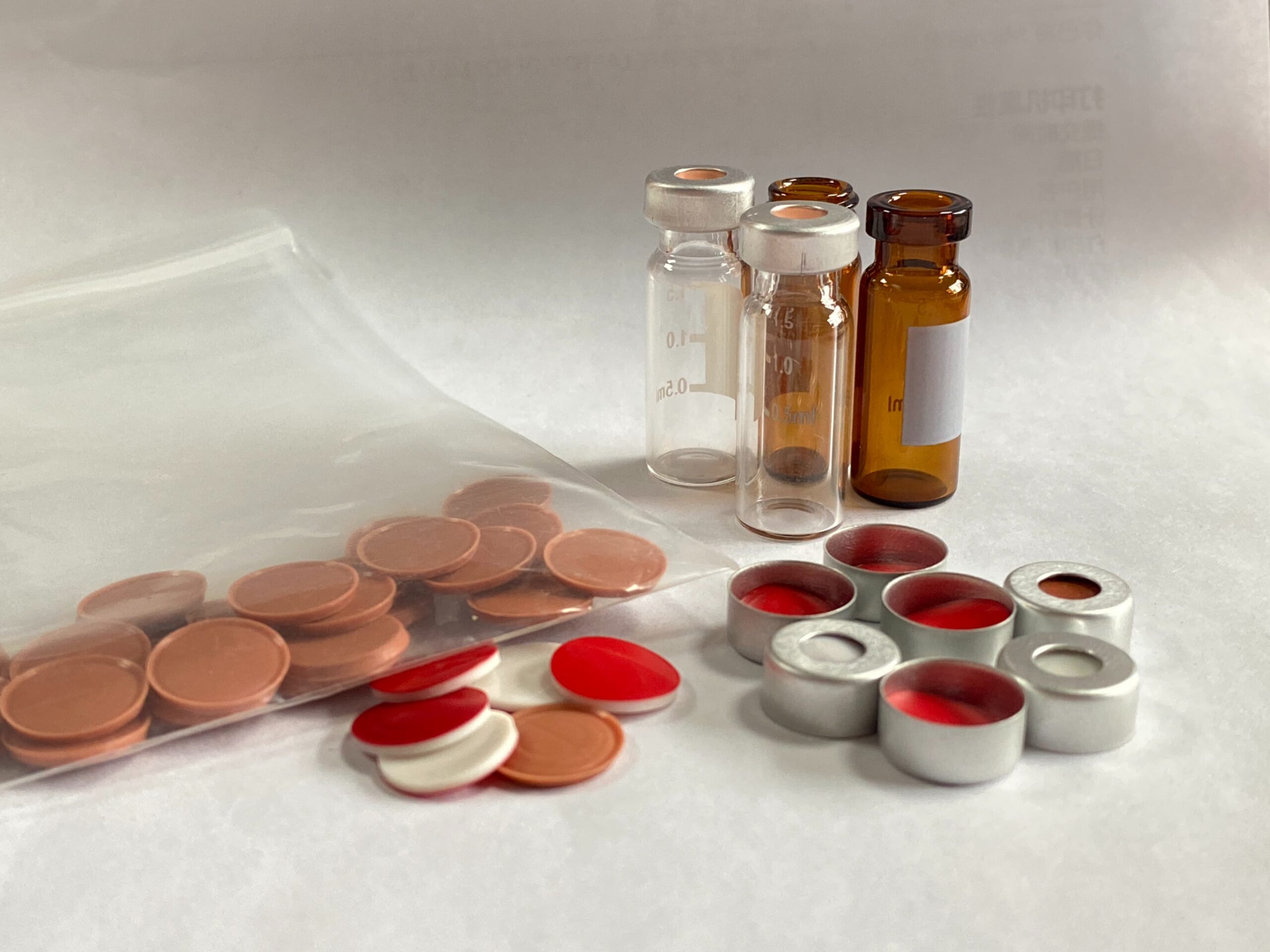
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene): PTFE is known for its excellent chemical resistance and is suitable for a wide range of solvents, including corrosive chemicals. It is often used in combination with other materials.
Silicone: Silicone septa are flexible and can be resealed after needle penetration, making them suitable for repeated injections. However, they may not be compatible with all solvents.
Butyl rubber: This material has good sealing properties, but has limited chemical resistance compared to PTFE.
PTFE/silicone composite: Combines the advantages of both materials, with good chemical compatibility and resealability.
2. Solvent Type
The type of solvent used will also influence septum selection:
Aqueous solutions: For water-based solvents, silicone or PTFE/silicone septa are often recommended due to their excellent compatibility.
Organic solvents: For organic solvents such as methanol or acetonitrile, PTFE or PTFE/silicone composites are preferred due to their excellent chemical resistance.
Corrosive chemicals: For highly corrosive solvents such as strong acids or bases, PTFE is often the best choice.
3. Sealing performance
The ability of a septum to reseal after a needle puncture is critical to maintaining sample integrity:
Slit vs. non-slit design: Some septa have slits to facilitate needle insertion, but this may affect the seal over time. Non-slit designs provide a tighter seal but may require more force when injecting.
Resealability: Look for septa that can effectively reseal after multiple needle punctures to prevent contamination and evaporation.
Want to know whether to choose septa in Pre-slit or Not? please check this article: How to Choose a Septa Pre-slit or Not?
4. Extractables and Leachables
When working with sensitive samples, it is critical to consider extractables and leachables in the septum material:
Low Extractables: Select septa with low extractables to minimize the risk of contamination. PTFE has low extractables compared to rubber-based materials.
Testing Standards: Some manufacturers provide data on extractables; review these specifications when selecting a septum.
5. High Temperature Resistance
Consider the temperature range in which your HPLC system will operate:
High Temperature: If your application involves high temperatures, make sure the septum material can withstand these conditions without degradation.
Cryogenic Applications: For cryogenic applications, select a material that maintains integrity at low temperatures.
6. Physical Properties
The physical characteristics of the septum can also affect performance:
Thickness: Thicker septa may provide a better seal but may require more force during needle penetration.
Hardness: Softer materials may provide better resealability but may be more susceptible to damage during repeated use.