The Differences of Static vs. Dynamic Headspace GC
Headspace gas chromatography (GC) is a powerful technique for analyzing volatile compounds in various matrices, from food and beverages to environmental samples. Within this realm, two primary methods exist: static and dynamic headspace GC. Understanding the differences between these two approaches can help you choose the right method for your specific analytical needs.
Static Headspace GC
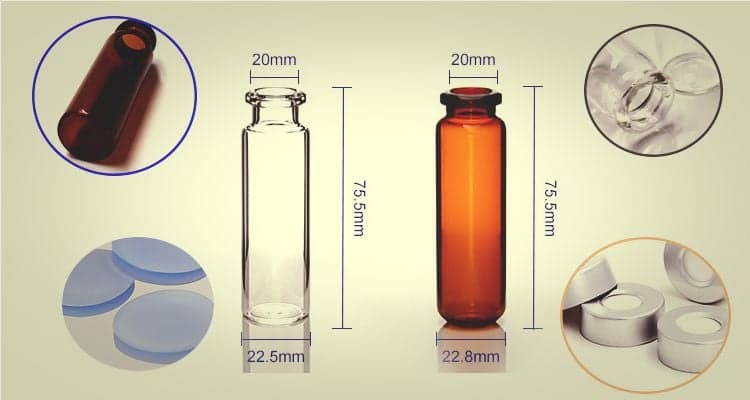
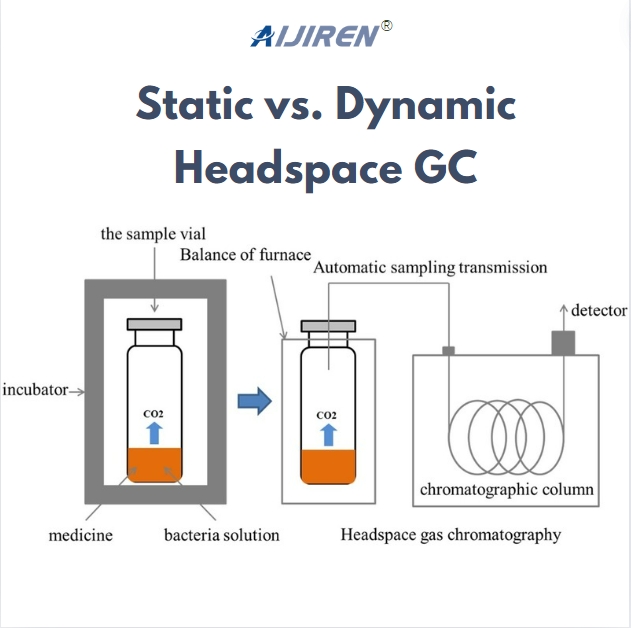
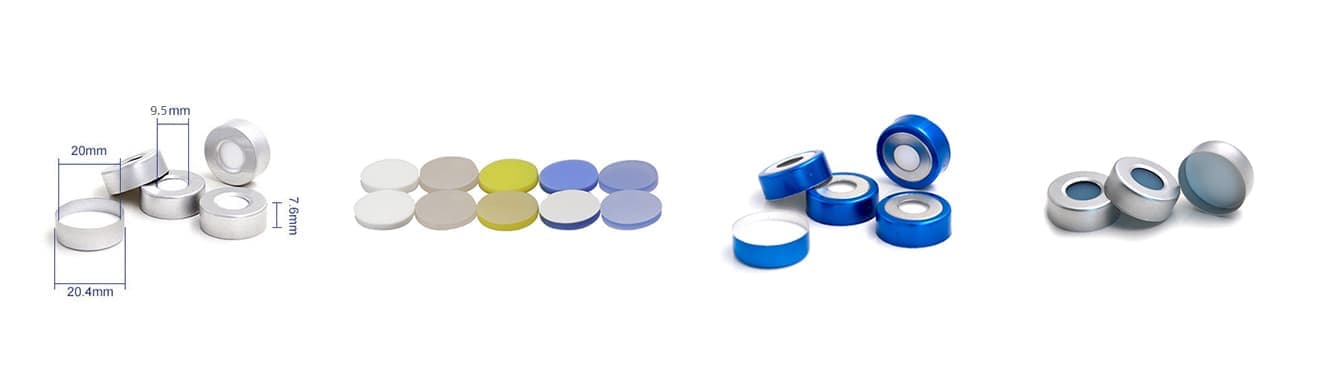
Principle: In static headspace GC, a sealed vial containing the sample is heated to allow volatile compounds to partition into the gas phase above the sample. A portion of this gas phase is then injected into the GC for analysis.
Advantages: This method is straightforward, requiring minimal equipment and sample preparation. It’s particularly effective for samples with low volatility and is commonly used in food and beverage analysis to detect flavor compounds and contaminants.
Limitations: Static headspace can be less sensitive for trace-level analysis since it relies on the equilibrium partitioning of volatiles, which may not capture all analytes present in the sample.
Dynamic Headspace GC
Principle: Dynamic headspace GC involves continuously purging the gas phase above the sample with an inert carrier gas, which sweeps volatile compounds into a trap or directly into the GC. This method enhances the concentration of analytes and improves sensitivity.
Advantages: Dynamic headspace is ideal for trace analysis and can capture a broader range of volatile compounds. It is particularly beneficial for environmental samples and complex matrices where sensitivity is critical.
Limitations: This method requires more sophisticated equipment and can be more time-consuming due to the need for continuous purging.
Conclusion