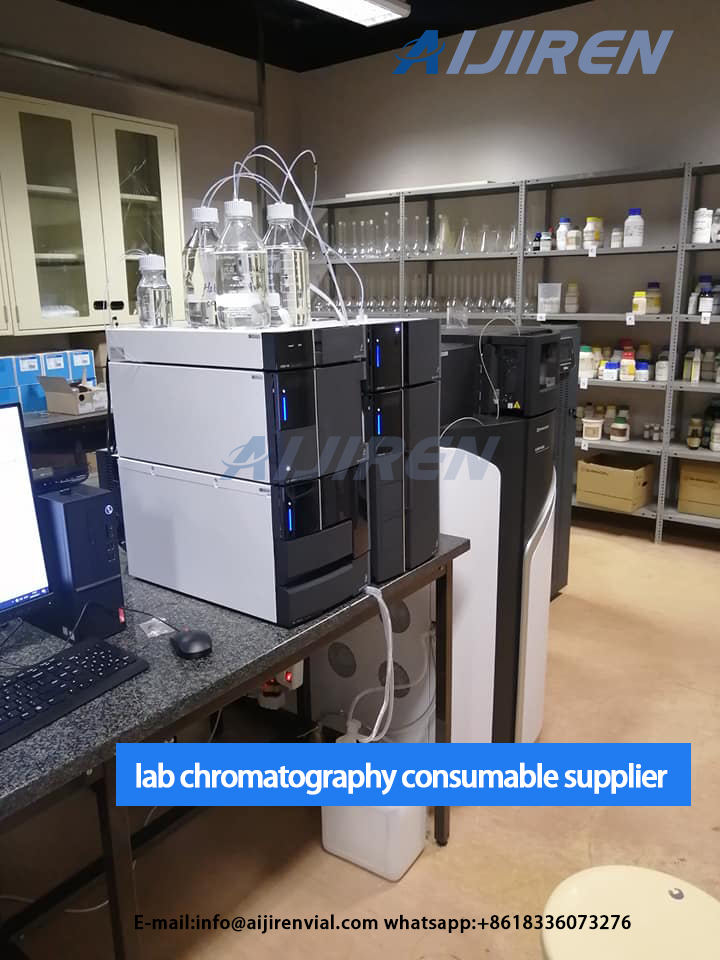
Understanding Peak Area in Gas Chromatography
In gas chromatography (GC), peak area is a key measurement that directly correlates to the amount of analyte present in the sample. Understanding the factors that affect peak area can help...
Contact US
Get Price
Share:
Content
In gas chromatography (GC), peak area is a key measurement that directly correlates to the amount of analyte present in the sample. Understanding the factors that affect peak area can help ensure that analytical results are accurate and reliable. Here are some key factors to consider:
1️⃣Injection volume
The amount of sample injected into the GC system can significantly affect peak area. Consistent injection volumes are critical for reproducibility. Variations can lead to inconsistent peak sizes, which can affect quantitative analysis. Using an autosampler can help maintain precision in injection volumes.
2️⃣Flow rate
Carrier gas flow rate plays a critical role in determining peak area. Higher flow rates result in sharper peaks with potentially larger areas, while lower flow rates can result in broader peaks with reduced areas. It is critical to optimize the flow rate for each specific analysis to achieve the best results.
3️⃣Column efficiency
Column performance directly affects peak shape and peak area. Factors such as column age, stationary phase conditions, and temperature can all affect efficiency. A degraded or contaminated column may produce broader peaks with reduced peak area, leading to inaccurate quantitation.
4️⃣Detector Sensitivity
The type of detector used in the GC can also affect peak area measurements. Different detectors have different sensitivities and response factors. For example, a flame ionization detector (FID) provides a response proportional to the mass of the analyte, while a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) responds based on concentration differences.
5️⃣Temperature Control
Temperature stability within the GC oven is critical to maintaining consistent retention times and peak areas. Fluctuations can cause changes in analyte volatility and retention behavior, affecting the overall chromatogram.
Conclusion
Understanding these factors is critical to optimizing GC methods and ensuring accurate quantitation of analytes. By controlling injection volume, flow rate, column efficiency, detector sensitivity, and temperature, you can improve the confidence of your chromatographic results.
Inquiry
More Headspace Vials